
What is Rancher?
Rancher is an open-source platform for managing and deploying docker containers and entire docker application stacks across multiple host systems. It bundles the power of many different technologies from the Docker environment, such as orchestration and scheduling frameworks Swarm, Kubernetes and pesos in one application.
Other docking applications (application stacks) from the in-house application catalog can be installed as additional central and useful components. Distributing a WordPress cluster is then done just as quickly as adding more host nodes to the Rancher cluster.
Rancher itself is also supplied as a docker container and can thus be installed in a child-friendly manner.
Step 1: Preparation and System Requirements
We use a setup from three servers in our example. A management server that will host the rancher server and two host notes on which the docker containers will be distributed later.
The setup for the agent server will be 2 CPU, 4GB RAM, and 50GB SSD Storage. For the two host nodes we choose 4 CPUs, 8GB RAM and 200GB SSD storage.
On all three systems we install Ubuntu 16.04 with docker as shown in the last tutorial.
https://gridscale.io/community/knowledgebase/docker-auf-ubuntu-16 -04-lts/
https://gridscale.io/community/knowledgebase/docker-auf-ubuntu-16 -04-lts/
Hint: If you build your setup on gridscale, you do not need to do the setup thrice. After you have installed the first server, you can simply make a snapshot of the storage, convert it to a template and install the other servers from it.
In your gridscale panel, that looks like this:

Step 2: Install Rancher
If we have docker installed on all three Cloud servers, there is actually not much to do. To install the management server agent, you must log on to the “agent” server via SSH.
If you are on the server, the following command is enough to install and run Rancher:
sudo docker run -d --restart=unless-stopped -p 8080:8080 rancher/server
Once the docker image is loaded and started, you can log in by browser.
http://<IP-ADRESSE>:8080
Here you can register.

I recommend that you set a good password directly in the menu item “Admin & gt; Access Control” or enable GitHub authentication.
Step 3: Add Host Nodes
Next, we need to add our two host nodes to the Rancher cluster so that the Docker containers can be distributed across both hosts.
To do this, go to the menu item “Infrastructure> Hosts” in the Rancher interface and click “Add Host”.

Select the URL to connect the host node to the Rancher server. We leave here the default value, since we have nothing else configured.
Select the type Custom here and enter the IP of the host system in field No. 4, which you want to add first.
Next, you need to do nothing more than run the command shown in point 5 on the first host node.
What’s happening now is the following: Another rancher docker image is launched that automatically connects to your management server.
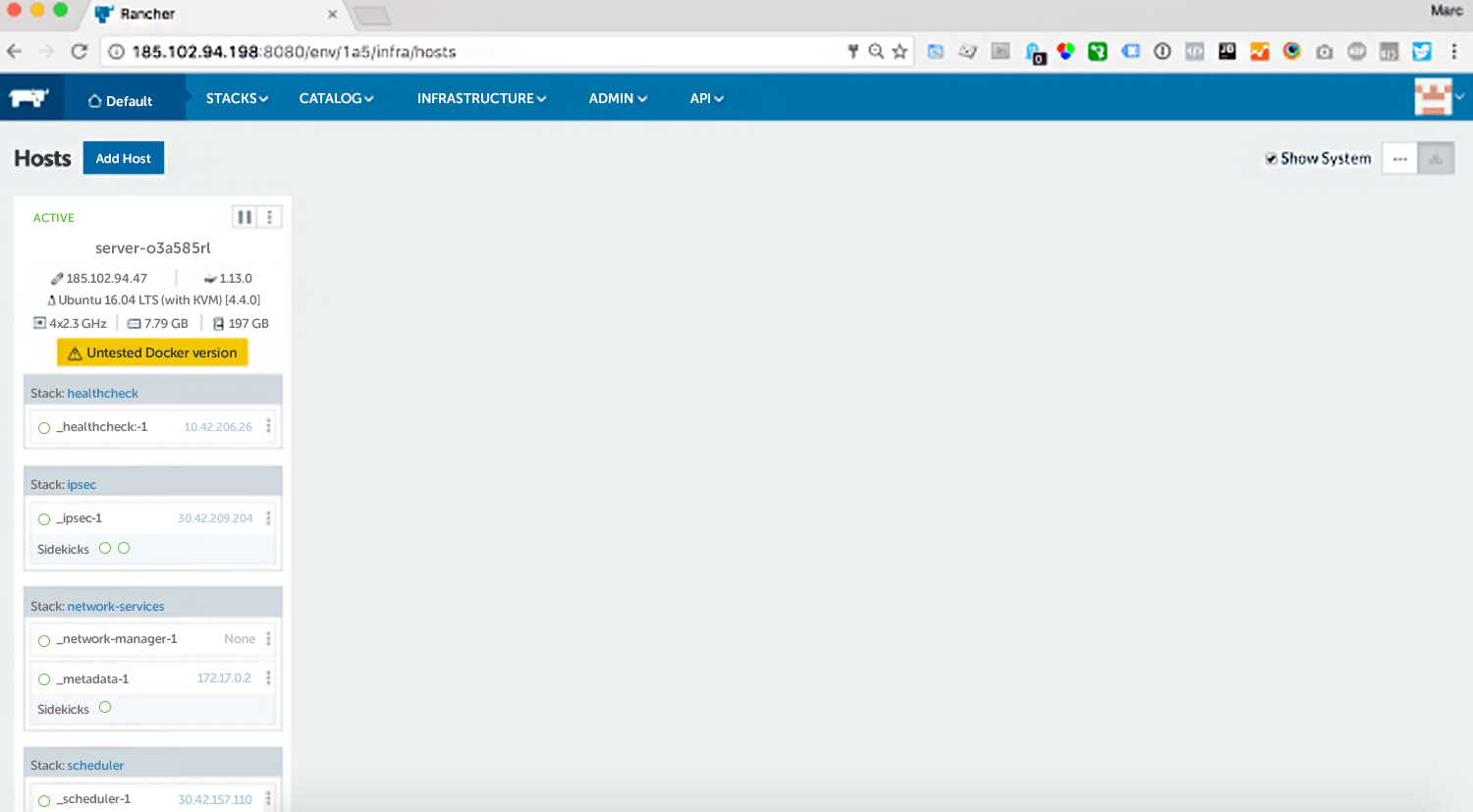
If you run the command in the host node console, it takes a few seconds for you to see a new host system under the Infrastructure> Hosts menu item.
(Since we have installed the latest version of Docker on our host, we now have a compatibility issue.)
For better order, you can give the host node a new name via the menu item “Edit” at the top right.
With the second Host Node you do exactly the same.
- Add Host
- Enter the IP address
- Command in the console of the second host node
- Wait until the host node appears in the Rancher interface
- Customize your name
- Finished

So quickly you have a rancher with 2 host nodes set. As you can see in the individual hosts, Rancher has automatically started some containers for the different rancher services.
Step 4: Install the distributed MariaDB Galera Cluster Setup
Next, let’s install an initial application. For this, we use the Rancher-Catalog. Here you will find a lot of pre-built applications, which you can configure and install directly in the interface.
Click on Catalog, look for MariaDB Galera Cluster and click on “View Details”.


Here you can only provide some information for the database. Passwords and the first user. Enter your data and click Create.
TIP: If you want to see what Rancher does exactly, see under preview that rancher-beside the well-known docker-compose.yml creates a rancher-compose.yml, in which the configuration is described. You can do this later. Export if you have adjusted the setup if necessary.
Now you can watch as Rancher does all the work for you. Rancher automatically distributes the containers on both host systems and starts all docker containers.
After a while the status of the stack should switch to active and you can see what Rancher has created exactly by clicking on the stack.

Here you can see the 13 Docker Container, Loadbalancer.
Now, when you go to the Hosts view, you see that Rancher has distributed the different containers across both systems to guarantee a fail-safe.

So quickly you can build up a distributed MariaDB Galera Cluster and scale it easily and flexibly. Adds further host systems later and increases the number of individual containers directly via the Rancher interface.

So quickly you can build up a distributed MariaDB Galera Cluster and scale it easily and flexibly. Adds further host systems later and increases the number of individual containers directly via the Rancher interface.
I hope you enjoy experimenting!
PS: If your rancher wants to test with gridscale, you can use the voucher “welcome” after logging in to get 10 € credit.
https://my.gridscale.io/signup
https://my.gridscale.io/signup




0 Comments